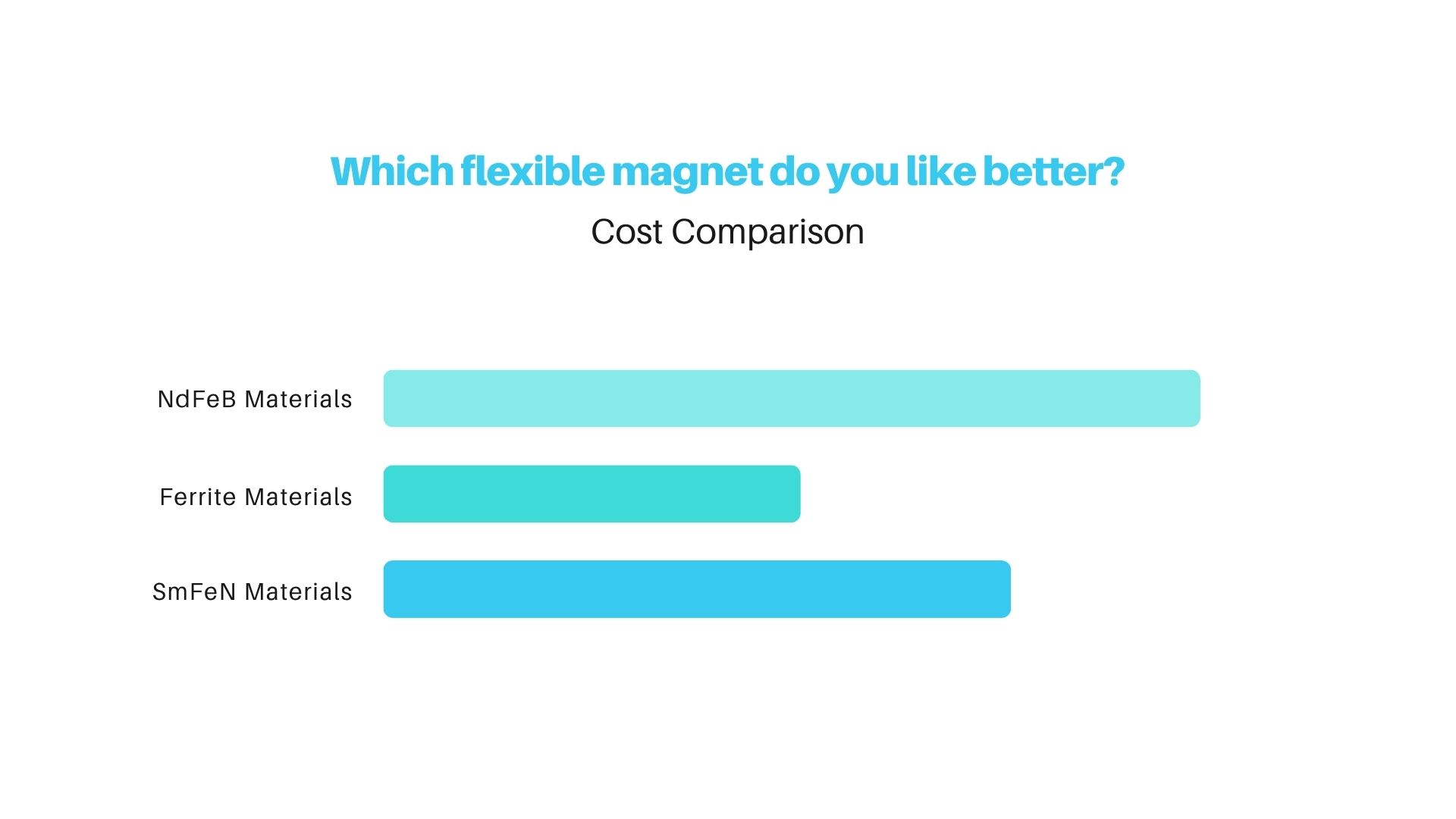
How to flush a toilet when the handle is broken ?
The toilet is one of the most frequently used fixtures in any bathroom. After long-term use, it’s not uncommon to encounter broken components—like a flush handle that no longer works because the internal mechanism has snapped. While this might seem frustrating, there’s no need to panic. With a few simple tricks, you can still flush your toilet without the handle and keep your bathroom clean and functional.
Here are some quick and practical ways to flush your toilet when the handle is broken.
Step 1: Understand How the Toilet Handle Works
The flush handle might look like a small part, but it’s actually the trigger of the entire toilet flushing system. It’s connected to a lift rod or chain inside the tank. When you press the handle, it pulls up the toilet flush valve flap or canister, allowing water to rush from the tank into the bowl to flush waste away.
Understanding this mechanism will help you operate it manually when the handle stops working.
Step 2: Three Manual Flushing Methods You Can Try
1. Pull the Chain Inside the Toilet Tank
First, remove the toilet tank lid. You’ll see a chain connecting the handle to the flush valve—this chain might be plastic or stainless steel.
Gently pull the chain upward with your hand. This action opens the flush valve and lets the water flow into the bowl, effectively flushing the toilet. Once flushing is complete, simply release the chain and let it drop back into place.
This is the most straightforward temporary solution. Just be careful not to yank too hard, as excessive force can damage the flush valve or break the chain.
2. Lift the Flapper or Canister Directly
If the handle stopped working because the chain snapped (which often happens with plastic chains), then method one may not work. In that case, you can manually lift the toilet flapper or canister directly by hand.
Lifting it fully will open the flush valve and allow water to exit the tank. Once the flush is complete, gently lower the flapper back into place. Be careful not to let the broken chain fall into the drain hole—this could prevent the flapper from sealing properly and cause the toilet to leak.
3. Use a Bucket to Flush the Toilet
If you don’t want to mess with the tank at all, here’s a traditional approach: flush with a bucket of water.
Fill a bucket with about 6 liters (or 1.5 gallons) of water—that’s approximately the full flush volume of most toilets. Quickly pour the water into the bowl from a height, aiming for the drain hole. This creates a forceful rush of water that mimics the effect of a regular flush and clears the waste.
Pour quickly but carefully to avoid splashing dirty water, and make sure to pour directly into the center of the bowl for the best results.
Step 3: What to Do After the Temporary Fix
While the above methods are great for emergencies, they’re not permanent solutions. Manually opening the tank every time is inconvenient and can potentially damage internal components.
You should replace the toilet handle as soon as possible. Many universal toilet tank levers are available online—Amazon has a wide selection to choose from. If you're not confident about installing one yourself, consider hiring a plumber.
You can also check out our website, where we provide video tutorials on how to install different types of toilet flush handles.
Final Thoughts: Don’t Panic When the Handle Breaks
A broken toilet handle isn’t the end of the world. Once you know the right tricks, you can flush your toilet just fine and keep everything hygienic until a repair is done.
Regularly inspect your toilet’s internal components to catch small issues before they turn into big problems. And if you're in need of quality toilet replacement parts, feel free to explore our product page for handles, valves, and more.